As the sun sets and darkness envelops the world, human activities don't necessarily come to a halt. Indeed, many tasks, whether they're of a professional nature or personal interest, continue into the night. Night vision technology has been instrumental in facilitating these tasks, extending our sight beyond the constraints of natural light. Whether you're a security professional ensuring safety in the dark, a wildlife enthusiast observing nocturnal creatures, or a civilian navigating the outdoors at night, night vision devices have revolutionized how we interact with the world after sundown.
How Does Night Vision Work?
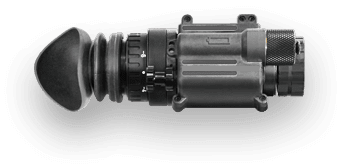
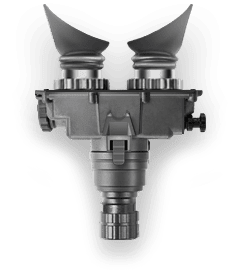
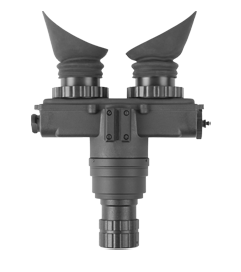
At its core, night vision technology transforms the seemingly impenetrable dark into a world illuminated by the faintest light. Whether for the military on a covert operation or a wildlife enthusiast tracking nocturnal animals, night vision equipment serves as an invaluable tool, overcoming the human eye's limitations in low-light conditions. The science behind night vision involves harnessing ambient light—such as moonlight or starlight—that may be invisible to the naked eye. These devices operate by capturing this sparse light through an objective lens, which then hits a light-sensitive surface known as a photocathode. The photocathode converts the photons into electrons, amplifying them to create a detailed image despite the prevailing darkness. Infrared light, which is undetectable by the human eye, is another crucial component for some night vision systems. Devices equipped with an infrared illuminator can emit this light, bouncing it off objects to create an image even in total darkness.
Digital Night Vision vs Traditional Night Vision
While the underlying principle is the same – making the unseen seen – the approach differs between traditional (also known as analog) and digital night vision. Traditional night vision devices, often referred to as Gen 1, Gen 2, and Gen 3, use the photocathode method described earlier. Each successive "gen" represents advancements in technology, with Gen 3 offering the highest performance but also at a higher cost.
On the other hand, digital night vision devices work more like a digital camera. They capture the light through an objective lens, convert it into a digital signal, and then display the image on a screen. This digitization process allows for several advantages, including the ability to record images or video, and less risk of damage from exposure to bright light. However, the choice between digital and traditional night vision depends on the user's specific needs, budget, and intended application.
Can a Civilian Own Night Vision?
Despite its initial development for military use, night vision technology is now available to civilians. From wildlife observation and nighttime navigation to home security and search and rescue, the applications are as diverse as the users themselves. Whether you're a civilian interested in astronomy or a professional seeking to enhance your nighttime operations, you'll find a range of night vision for sale, each designed to suit different needs and budgets.
However, it's essential to be aware of any local laws or regulations pertaining to the use or ownership of such devices. In conclusion, night vision technology, whether analog or digital, serves a crucial role in various fields. As a product of continuous technological advancements, it promises to further redefine how we operate in the dark, making the unseen seen.
Unveiling the Unseen: The Impact of Night Vision
The advent of night vision has significantly impacted various sectors. In law enforcement and security, it has empowered officers to maintain safety under the cloak of darkness. For wildlife enthusiasts and researchers, it has opened a window into the intriguing world of nocturnal animals. Moreover, night vision technology has enhanced outdoor activities such as camping and hiking, offering safer navigation after sundown. The potential applications are vast and continually evolving, making night vision a truly transformative technology.